Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have taken the gaming industry by storm, offering immersive experiences that place players in dynamic, interactive environments. However, designing user interfaces (UI) for VR and AR games presents unique challenges. Unlike traditional game UIs, VR and AR require intuitive, responsive designs that integrate seamlessly into the player’s real-world space or virtual environment.
In this article, we will explore how Armature, a powerful wireframing tool, simplifies the process of creating game UIs for VR and AR. We’ll cover the basic principles of VR/AR UI design, the unique considerations these interfaces require, and how Armature helps developers create efficient, immersive, and user-friendly designs.
What Makes VR and AR UI Design Different?
In traditional 2D game design, the user interface is confined to a screen. However, VR and AR interfaces need to bridge the gap between the real world and the virtual experience, resulting in a unique set of design considerations. Key differences in VR and AR UI design include:
- Immersion: In VR, the user is completely immersed in a virtual environment. UI elements must feel as if they are part of the virtual world and should not disrupt the player’s sense of immersion. Similarly, AR integrates virtual elements into the real world, which means the UI must adapt to different physical spaces and respond in real-time.
- Spatial Awareness: In both VR and AR, users interact with UI elements through spatial movements, such as head tilts, hand gestures, or eye tracking. Therefore, UI elements must be designed to work seamlessly with the user’s natural movements, ensuring that interaction feels intuitive and fluid.
- 3D Design: While 2D UI elements like buttons and menus work well in traditional games, VR and AR UIs often require 3D elements. Designing buttons, sliders, and other interactive elements in three-dimensional space can be challenging, as these elements need to be easily reachable and visible without disrupting the experience.
Armature helps address these challenges by offering the right tools and design templates to build immersive, efficient, and user-friendly VR and AR UIs.
Step 1: Understanding the Key Elements of VR and AR UIs

Before diving into Armature’s capabilities, let’s first understand the essential elements that make up a VR or AR UI. Some of the common UI elements in VR/AR games include:
- Floating Menus: These menus float in the virtual or augmented space and can be activated by hand gestures, eye movements, or controllers. They often serve as the main navigation tool within the experience.
- Interactive Objects: In VR and AR, UI elements can take the form of physical objects that the player can interact with. These could be buttons, switches, levers, or any item that requires user input.
- Progress Indicators: Whether it’s a health bar, score, or mission objective, progress indicators are essential in VR and AR games. They must be clearly visible but not intrusive, so they should be positioned carefully within the player’s view.
- Contextual Pop-ups: Contextual pop-ups provide information that appears when needed, such as help tips, status updates, or interactive tooltips. These must be dynamic and responsive to the player’s actions.
- Real-World Overlays: In AR, virtual objects and interfaces overlay on top of the real world. The challenge is to ensure these elements interact with the physical environment in a realistic and non-distracting way.
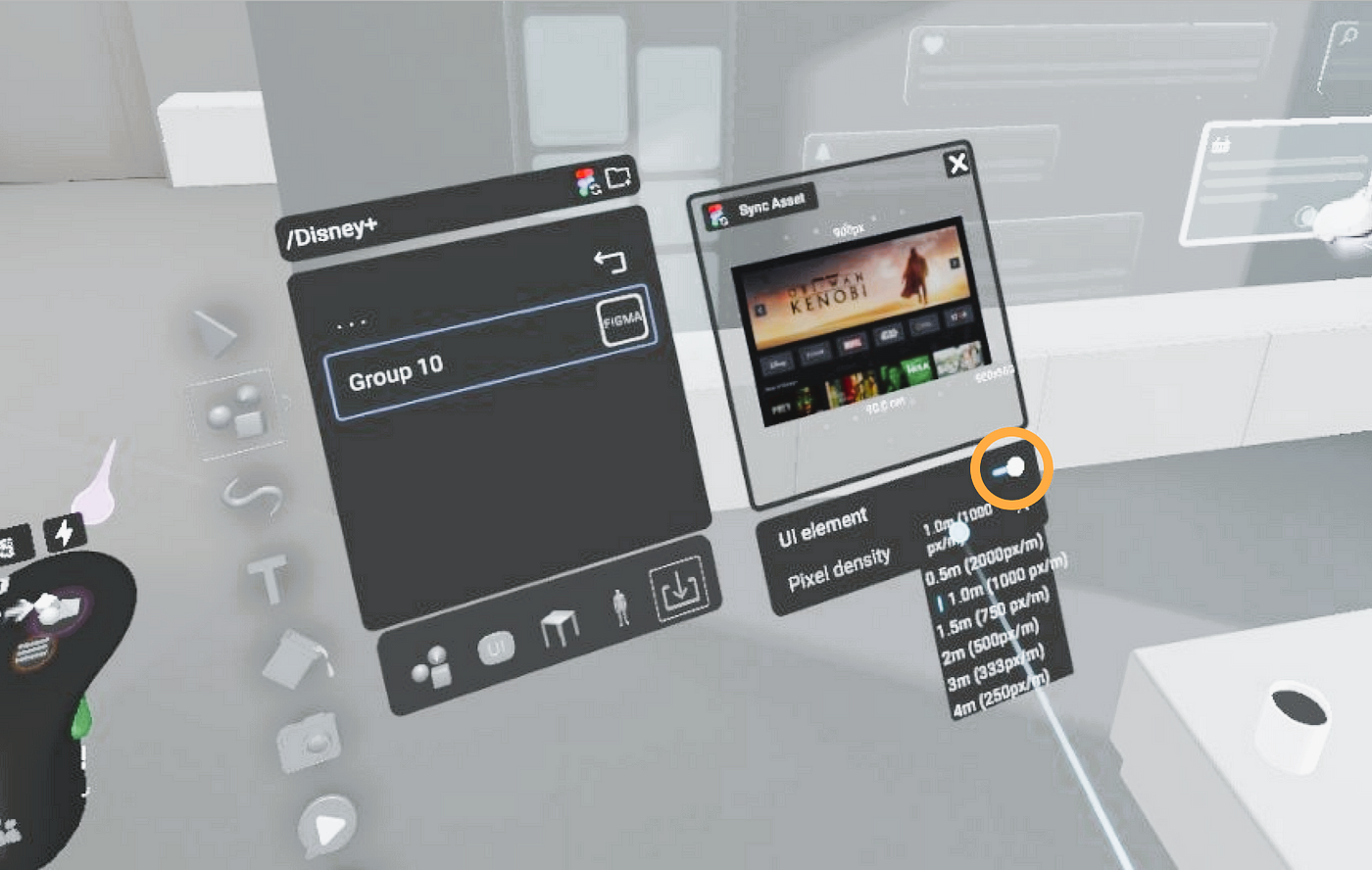
Step 2: Using Armature to Create VR and AR UI Designs
Armature is a robust design tool for game UI creation, and it’s especially useful for VR and AR development. Let’s go through how Armature makes it easy to create interfaces for these technologies. Read more about 5 common mistakes to avoid when designing game interfaces in our article.
1. Start with Ready-Made Templates
Armature provides a wide array of pre-built templates and components that are tailored for VR and AR interfaces. These include:
- Floating Menu Templates: Ready-made templates for floating menus that can be customized to fit your game’s theme and functionality. These menus can be adapted for VR, where they appear in 3D space, or for AR, where they align with real-world objects.
- Interactive Components: Armature offers buttons, sliders, and dials that can be easily customized for VR and AR. These components can be placed in the 3D space, ensuring they are responsive to player inputs.
- Health Bars and Progress Indicators: Use Armature’s progress bar components to display health, score, or mission objectives. These can be placed within the virtual environment or projected in AR based on your game’s needs.
2. Customizing 3D UI Elements
Unlike traditional 2D interfaces, VR and AR UIs require a 3D design approach. Armature offers tools to design interactive elements that work seamlessly in three-dimensional space.
- 3D Panels and Widgets: These can be manipulated in 3D space, rotated, and scaled to fit the game environment. You can position them at any depth, making them accessible but not overwhelming.
- Depth and Scale Adjustments: With Armature, you can easily adjust the depth and scale of UI elements. This is crucial in VR, where the player’s perception of space must be considered to avoid causing discomfort. For AR, the scale of the UI elements should be adaptable to various physical environments.
3. Layering for Immersion
One of the core principles of effective VR and AR UI design is immersion. Armature allows you to layer UI components with ease. You can overlay virtual UI elements onto your game’s environment without breaking the player’s immersion.
- Depth of Field: Adjust the layering of UI elements so they appear as if they belong in the game world. For instance, place important HUD elements within the player’s immediate view, while less critical info can be positioned farther away.
- Dynamic UI Elements: Armature also supports dynamic UI designs. For instance, progress bars or health indicators can change based on the game’s state. These can animate or fade in and out depending on the context, improving the user experience.
4. Exporting to VR and AR Game Engines
Once you’ve designed your UI, Armature simplifies the export process. You can export your assets to major game engines such as Unity and Unreal Engine, which are both extensively used for VR and AR development.
- Unity: Armature’s export functionality is fully compatible with Unity, which supports both VR and AR interfaces. Once exported, you can integrate your UI elements into your Unity project and adjust them according to the specific VR or AR environment.
- Unreal Engine: Armature also supports Unreal Engine, another popular choice for VR and AR games. After exporting the UI assets, you can integrate them into Unreal Engine’s interface system, using Blueprints or C++ to ensure smooth interactions.
Step 3: Best Practices for VR and AR UI Design
When designing VR and AR UIs with Armature, it’s important to keep a few best practices in mind:
- Optimize for Comfort: In VR, UI elements that are too close to the player can cause discomfort. Ensure UI elements are positioned at a comfortable distance, and avoid placing them in the peripheral vision where they may induce motion sickness.
- Focus on Interaction: VR and AR UIs must be intuitive. Use gestures, voice commands, or eye tracking to create interactive elements that respond to player inputs naturally.
- Test Across Platforms: VR and AR interfaces may behave differently depending on the hardware (e.g., Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or Microsoft HoloLens). Always test your UI on multiple platforms to ensure compatibility and performance.
- Maintain Simplicity: In both VR and AR, a cluttered UI can detract from the immersive experience. Keep interfaces clean and minimal, only showing essential information at the right time.
Designing game UIs for VR and AR is an exciting but complex task that requires careful consideration of space, interaction, and immersion. Armature simplifies this process by offering ready-made templates, customizable 3D elements, and easy export options, making it easier for developers to create intuitive, immersive interfaces for VR and AR games.
Whether you are building a VR title for the Oculus Rift or an AR game for mobile devices, Armature’s tools ensure that your UI elements will enhance the player’s experience, seamlessly blending into the virtual or augmented world.
For more information on VR and AR UI standards and best practices, visit Wikipedia’s page on Augmented Reality.